Aggregate Queries in Oracle
Aggregate queries in Oracle operate on multiple rows of data, in contrast to scalar functions that work on individual rows.
There are five commonly used aggregate functions in SQL:
- MAX(): Returns the maximum value from a set. Works for numeric, character, and date/time types.
- MIN(): Returns the minimum value. Behavior is similar to MAX.
- SUM(): Calculates the total. Applicable only to numeric columns.
- AVG(): Calculates the average. Works only for numeric data types.
- COUNT(): Returns the number of rows. Can be used on any data type.
Let's create the following table to demonstrate aggregate queries:
CREATE TABLE Cricket_Scores (batsman VARCHAR(100), InningsNo INT, MatchType VARCHAR(10), score INT);
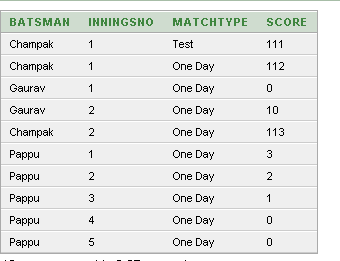
Sample Records
Example Queries

When using aggregate functions with other columns, you must include a GROUP BY clause.

Summary
Aggregate functions help in summarizing data such as totals, averages, or counts across multiple rows. They are essential for reporting and analysis in any SQL-based system.










0 Comments